Installing Services
This page describes how to create services.
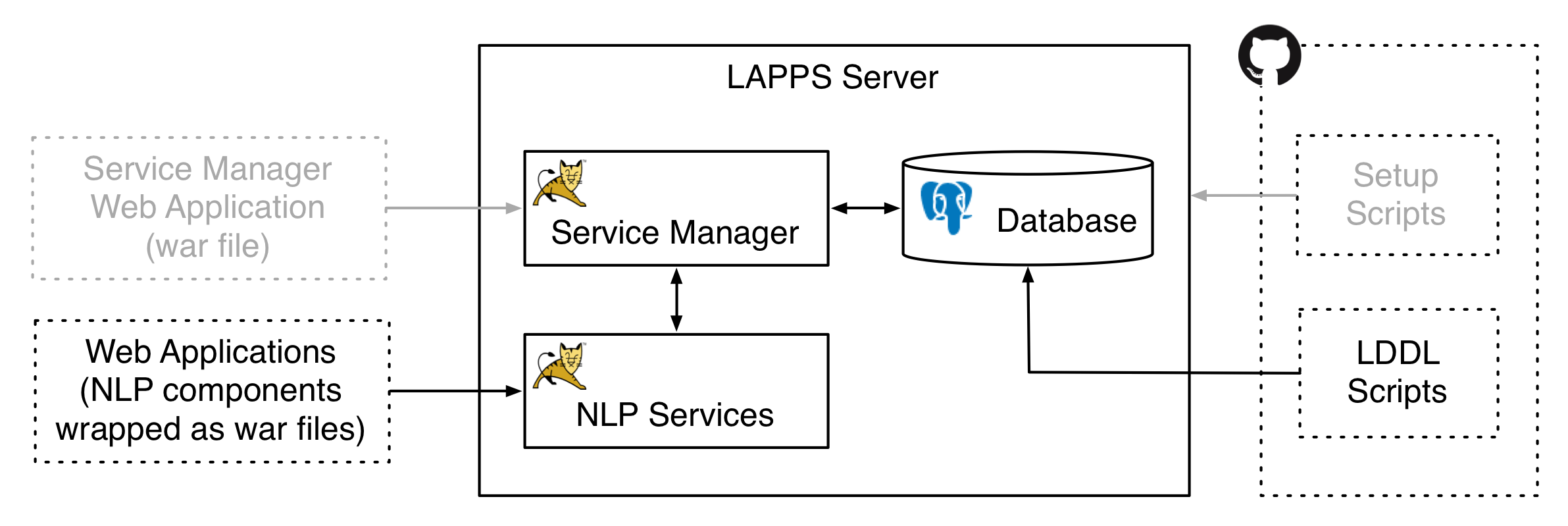
Adding a service to the LAPPS Grid involves various things:
- Wrapping the service as a Web Application. In essence this is about creating a WAR file, but it also requires the developer to know about Lappsgrid Exchange Datastructures (LEDs), the LAPPS Interchange Format (LIF), the Web Sevices Exchange Vocabulary (WSEV), and the use of discriminators.
- Deploying the service.
- Registering the service with the Service Manager.
1. Wrapping a Service
There are extensive notes on how to wrap a service at https://github.com/lapps/org.lappsgrid.examples. Those notes are set up as a series of steps and each time you click a next step then the code associated with that step will be available in the repository. The result of all those steps can be obtained as follows:
$ git clone https://github.com/lapps/org.lappsgrid.examples
$ git checkout step5
$ mvn clean package
We are assuming that you use Maven for building your project. Given the project object model file (POM file) in the repository, the mvn clean package command will create a war file named target/YOUR_ARTIFACT_NAME.war, if you had followed the instruction you would have changed that name at some point.
You can actually do the same (without the checkout step) with any of the repositories that implement a wrapped service, including:
- https://github.com/oanc/org.anc.lapps.stanford
- https://github.com/oanc/org.anc.lapps.gate
- https://github.com/brandeis-nlp/edu.brandeis.cs.stanfordnlp-web-service
- https://github.com/brandeis-nlp/edu.brandeis.cs.opennlp-web-service
All these repositories will be moved to the https://github.com/lappsgrid-services organization.
In the rest of this section we give a bit of high-level background on what services consume and create.
Lappsgrid Exchange Datastructures (LEDs)
All strings passed to and from LAPPS services are JSON strings containing LEDs, which are implemented as Data objects in org.lappsgrid.serialization.Data. Each LED consists of a discriminator, a dictionary of parameters and a payload. We will ignore the parameters here for now since most services do not use them and focus on the discriminator and the payload. The discriminator is used to determine how the contents of the payload should be interpreted (see below for more about discriminators). In general, a discriminator is a URI from the LAPPS Web Service URI Inventory at http://vocab.lappsgrid.org/discriminators.html. The dicriminator used in a LEDS is a special kind of discriminator since it is restricted to be one of a dozen or so media discriminators in the URI inventory. For example, the gate discriminator refers to http://vocab.lappsgrid.org/ns/media/xml#gate and instructs the service that the payload is to be interpreted as a GATE data structure.
Here is a simple example of a LED:
{
"discriminator": "http://vocab.lappsgrid.org/ns/media/text",
"payload": "Comments should be received no later than 3:00 PM EST on Sunday, August 26.\n"
}
In this case the discriminator instructs the service that the payload is plain text.
LAPPS Interchange Format (LIF) and Web Sevices Exchange Vocabulary (WSEV)
- output of wrapped components should follow LIF specifications and use elements from WSEV
- LIF specifications
- LIF JSON-schema
- WSEV at http://vocab.lappsgrid.org/
- WSEV discussion
- WSEV issues
The WSEV, also know as the LAPPS Vocabulary or simply the Vocabulary, …
Discriminators and the LAPPS Vocabulary
Discriminators are used in two places. Above we explained their use in the Lappsgrid Exchange Datastructures, where they acted as a way to tell services how to interpret the payload.
The other role for discriminators is in the produces and requires sections of a tool wrapper’s metadata and it is a way for the tool to tell the rest of the world what it needs and what it creates. Some of the discriminators used here refer to elements of the LAPPS Vocabulary. While it is true that each element of the vocabulary is associated with a discriminator, the reverse is not true.
It is up to the tool wrapper to check whether the input has what it needs by searching the contains section of the metadata section of a view.
More details on this, including on how to change the discriminator inventory and the vocabulary can be found on the Discriminators and the Vocabulary page.
2. Deploying a Service
Simply put the war file in the webapps directory under a Tomcat server set up for the service. This is also explained in the wrapping manual in github.com/lapps/org.lappsgrid.examples under step 4 near the end. After deploying a war file to Tomcat the new war will be deployed automatically (however, if you changed Java versions while running a tomcat server then you do need to restart Tomcat).
3. Registering a Service
You register services with the Service Manager by using LDDL scripts like the ones at https://github.com/lappsgrid-incubator/lddl-scripts. LDDL is the LAPPS Database Description Language, which is a Groovy DSL (Domain Specific Language) that can be used to initialize a LAPPS Grid database. See [http://www.lappsgrid.org/software/lddl/] (http://www.lappsgrid.org/software/lddl/) for more information on LDDL.
To run LDDL scripts you need the LDDL jar that you can create from the code at https://github.com/lappsgrid-incubator/org.anc.lapps.lddl.
$ git clone https://github.com/lappsgrid-incubator/org.anc.lapps.lddl
$ cd org.anc.lapps.lddl/
$ make jar
$ cp target/lddl-1.3.4.jar ~/bin
You can now take the main LDDL script at src/main/resources and edit it by replacing __VERSION__ by the current version number. Then put the lddl script somewhere and make sure that location is on the path.
$ sed 's/__VERSION__/1.3.4/g' src/main/resources/lddl > lddl
$ chmod +x lddl
$ mv lddl ~/bin
$ export PATH=~/bin:$PATH
https://github.com/lappsgrid-incubator/org.anc.lapps.lddl
Use the lddl-scripts in https://github.com/lappsgrid-incubator/lddl-scripts
Register using LDDL to update the service on the service manager on vassar or brandeis servers. Using Brandeis.lddl for Brandeis in lddl-scripts. Brandeis.lddl refers to lddl scripts in the brandeis subdirectory, thise would typically be changed or scripts would be added there for deploying new tools. There is a fork of this on brandeis-nlp, will probably rplace that by using a brandeis branch on lappsgrid-incubator.
We are still assuming old version of the service manager
The lddl-scripts/Update.lddl script takes another script from brandeis or vassar and installs/updates just that module
check whether this works with new service manager
- there is a cleanup script that cleans out the database but with the new database there may be new fields that ar enot cleaned up.