Overview of the LAPPS Grid Universe
The core of the LAPPS Grid consists of a Service Manager that connects to web services and a LAPPS Galaxy frontend that connects to one or more Service Managers. The main LAPPS/Galaxy site at http://galaxy.lappsgrid.org/ is a Galaxy frontend that points to several Service Managers. The LAPPS Grid has also been deployed using Docker images on Jetstream (https://jetstream-cloud.org/) and on Amazon Web Services (https://aws.amazon.com/). This page gives an overview on the structure of a LAPPS Grid and gives pointers to installation notes.
The Service Manager and its NLP Services
The Service Manager handles requests for service invocations and controls access to services. It also allows federation with other Service Managers so that services accross Service Managers can be accessed through a single point. The image below shows a LAPPS Server with two Tomcat instances and a Postgres database. One Tomcat instance hosts the Service Manager web application which has access to a PostgreSQL database as well as another Tomcat instance with NLP components wrapped as web applications. The PostgreSQL database stores information on what services there are and where they reside. The NLP services do not have to be on a different Tomcat instance on the same server, they could be on the same Tomcat instance as the Service Manager or on a Tomcat instance on a different server. It is also not required that the Tomcat server is used, but all our implementations have used Tomcat.
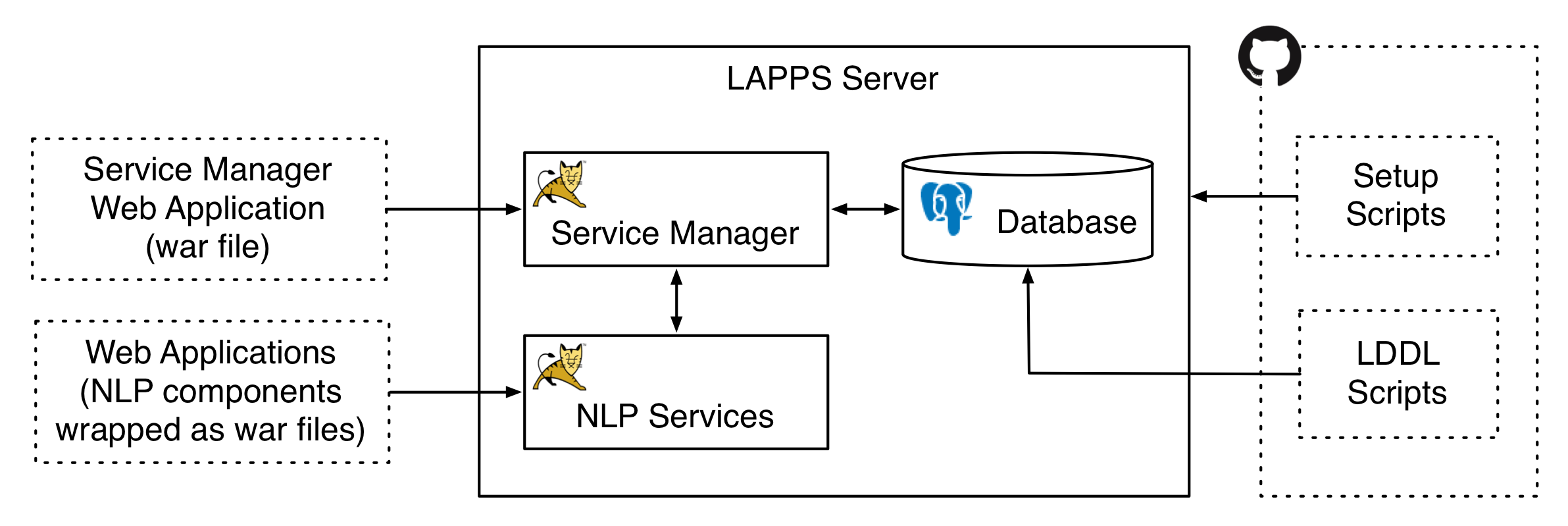
The dotted boxes give some indication on what was used to create the Service Manager and the NLP Services. The server is prepped for the LAPPS Grid by a couple of setup scripts and the Service Manager is put on the Tomcat server by uploading a WAR file (Web Application Archive). Similarly, for an NLP component to function in the LAPPS Grid it is wrapped in a WAR file and uploaded to the server. The LDDL scripts (LAPPS Database Definition Language) add entries to the PostgreSQL database that the Service Manager uses to invoke those services. See the following two pages for more details on this, in particular details on how to install and maintain the servers:
With the Service Manager and its services in place, you can access and run services using something like SoapUI or other tools (given the proper credentials). But for the LAPPS Grid the best way to access the services is through a Galaxy portal.
The LAPPS/Galaxy Frontend
Galaxy is used by the LAPPS Grid as the interface for creating workflows and for evaluating and sharing results. The LAPPS/Galaxy server points at one or more LAPPS Servers with a Service Manager, in the example below the portal uses two LAPPS Servers.
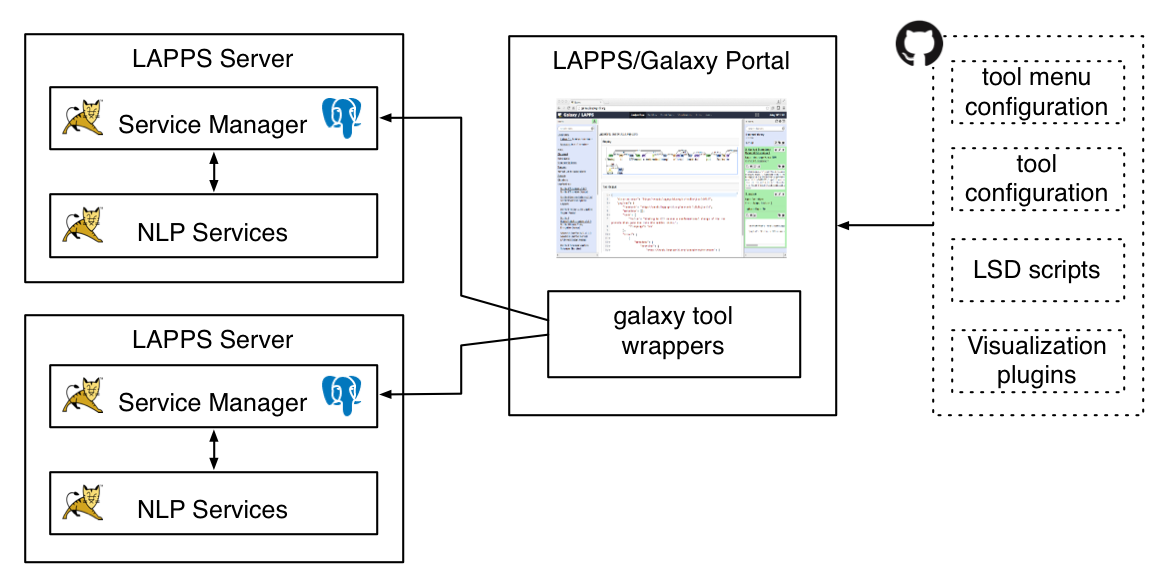
The LAPPS/Galaxy portal is built from a couple of Github repositories that contain a fork of the repository of the Galaxy Project at https://github.com/galaxyproject/galaxy as well as several additions including the following:
- Configuration files.
- LSD scripts to connect to LAPPS servers.
- Several visualization plugins.
Typically the LSD scripts connect to web service endpoints defined by the Service Manager, but it is actually possible to have them connect directly to the NLP web services.
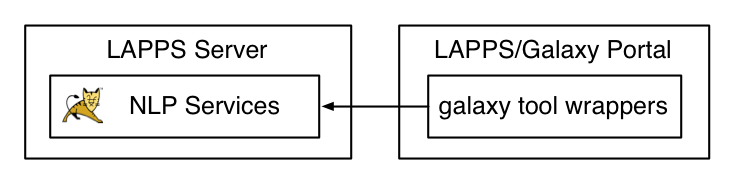
This setup is useful for those cases where the functionality provided by the Service Manager is not needed.
See Setting up Galaxy for more details including installation pointers.
The LAPPS Grid as Docker Containers
To increase portability we have created Docker images for components of the LAPPS Grid so that the LAPPS Grid can also be deployed as a set of Docker containers.
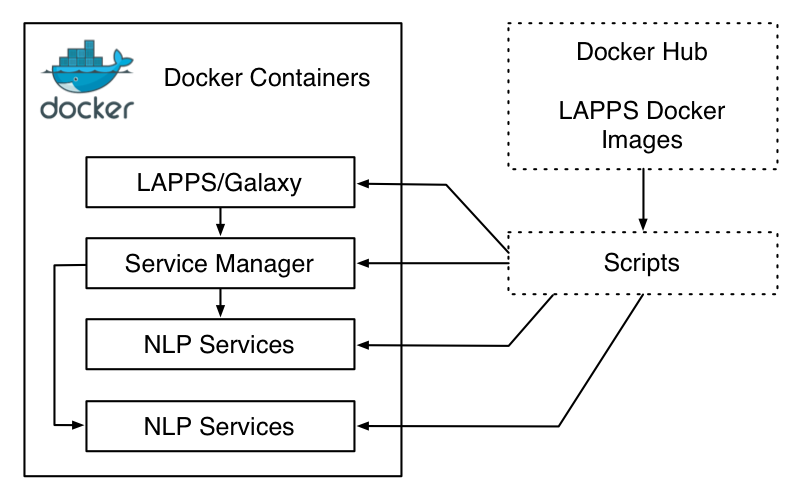
Any one can create their own Docker images and build a LAPPS Grid for a specific purpose. See Creating and Using Docker Images for more details.